Diet Plan For Glycogen Storage Disease The hepatic glycogen storage diseases GSDs are a group of disorders where abnormal storage or release of glycogen leads to potentially life threatening hypoglycemia and metabolic disturbances Dietary interventions have markedly improved the outcome for these disorders from a previously fatal condition to one where people
The following is a recommended general nutrition guideline for those with GSDIII to help maximize blood sugar control nutrition energy and hopefully minimize muscle damage for those with GSDIIIa Dietary treatment has been the cornerstone of disease management since the introduction of continuous glucose therapy by continuous enteral feeding and consumption of uncooked cornstarch UCCS in the 1970s and 1980s respectively 3 4 5
Diet Plan For Glycogen Storage Disease

Diet Plan For Glycogen Storage Disease
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Elroy-Weledji/publication/272623878/figure/tbl3/AS:613862252494848@1523367574262/Glycogen-storage-diseases.png

Glycogen Storage Disease Causes Types And Treatments Perfect Keto
https://perfectketo.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/type-0-1024x1024.jpg
Glycogen Storage Diseases
https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glycogenstoragediseases-150608120803-lva1-app6892/95/glycogen-storage-diseases-18-1024.jpg?cb=1433765371
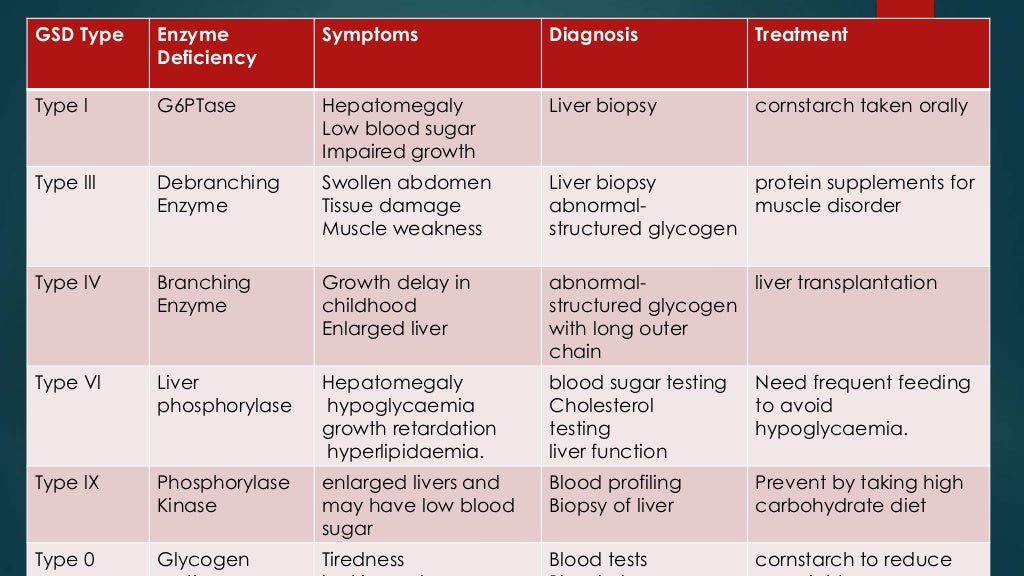
Management of Glycogen Storage Diseases 11 Feeding 11 Cornstarch 12 Illness or symptoms of hypoglycemia 13 Good dietary control to prevent low blood glucose is the most important part of the treatment It also controls urate and lactate Medication called Allopurinol can be used to reduce urate levels Untreated children can present with high Glycogen storage diseases GSDs also referred to as glycogenoses are inherited metabolic disorders of glycogen metabolism caused by deficiency of enzymes or transporters involved in the synthesis or degradation of glycogen leading to aberrant storage and or utilization The overall estimated GSD incidence is 1 case per 20000
Glycogen storage disease GSD type I also called Von Gierke disease results from a deficiency of glucose 6 phosphatase Type Ia or glucose 6 phosphatase translocase Type Ib preventing the production of glucose from glycogen stores during periods of fasting leading to severe hypoglycemia if untreated Dietary Management of the Glycogen Storage Diseases Evolution of Treatment and Ongoing Controversies Ross KM 1 Ferrecchia IA 1 Dahlberg KR 1 Dambska M 1 Ryan PT 1 Weinstein DA 1 Author information Affiliations 1 Glycogen Storage Disease Program Connecticut Children s Hartford CT USA 6 authors
More picture related to Diet Plan For Glycogen Storage Disease

Glycogen Storage Disorders Types Dandk Organizer
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320038085/figure/tbl1/AS:613906506592281@1523378125877/Classification-of-Hepatic-Glycogen-Storage-Diseases-and-Summary-of-Their.png

Glycogen Storage Diet
https://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009931004_1-fd99daaf3536c264532d086929bcc5e7-768x994.png
My Family Medicine Practice Introduction To Glycogen Storage Disease
https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-818BjgjjlOI/WRtu--J7drI/AAAAAAAAF4U/gI1HB70T-IgxWV7Q0x5tcXu9buRvY45GgCLcB/s1600/Glycogen%2Bstorage%2Bdisease.jpeg
Glycogen storage diseases GSDs are a heterogeneous group of inherited disorders caused by inborn errors of glycogen metabolism These disorders most commonly affect the muscle and liver where glycogen is the most abundant 1 For GSD I secondary metabolic disturbances include fasting hyperlactatemia hyperuricemia and The treatment mainly relies on dietary measures but there is however a greater fasting tolerance than in GSD type I Apart from the carbohydrate supply preserving gluconeogenesis requires an increased protein intake Goals of the national diagnostic and care protocol Aims
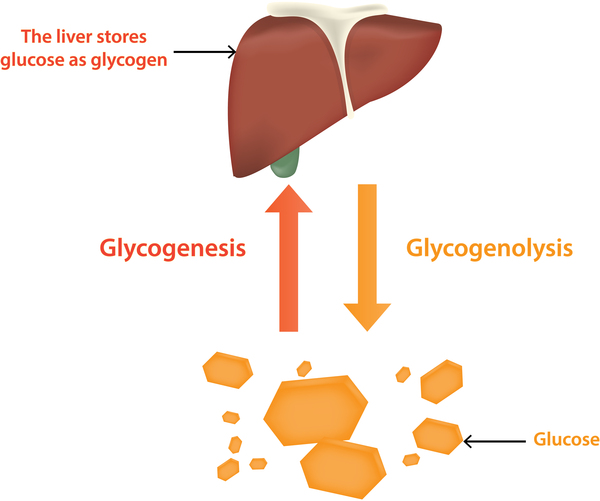
The hepatic glycogen storage diseases GSDs are a group of disorders where abnormal storage or release of glycogen leads to potentially life threatening hypoglycemia and metabolic disturbances Dietary interventions have markedly improved the outcome for these disorders from a previously fatal condition to one where people can do well with Glycogen storage disease types 1a and 1b GSD 1 are characterized by fasting hypoglycemia and elevated lactic acid uric acid cholesterol and triglycerides Patients with GSD type 1b are also at risk of neutropenia and inflammatory bowel disease

Medical Nutrition Therapy Diet Glycogen Storage Disease 1
https://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008807455_1-5af30b8a88d2b4881c68659beff16f8b-768x994.png

Muscle Glycogen And Exercise All You Need To Know INSCYD
https://inscyd.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Infographic-glycogen-level-scaled.jpg

https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7442342
The hepatic glycogen storage diseases GSDs are a group of disorders where abnormal storage or release of glycogen leads to potentially life threatening hypoglycemia and metabolic disturbances Dietary interventions have markedly improved the outcome for these disorders from a previously fatal condition to one where people

https://ufhealth.org/sites/default/files/media/GSD/General-…
The following is a recommended general nutrition guideline for those with GSDIII to help maximize blood sugar control nutrition energy and hopefully minimize muscle damage for those with GSDIIIa
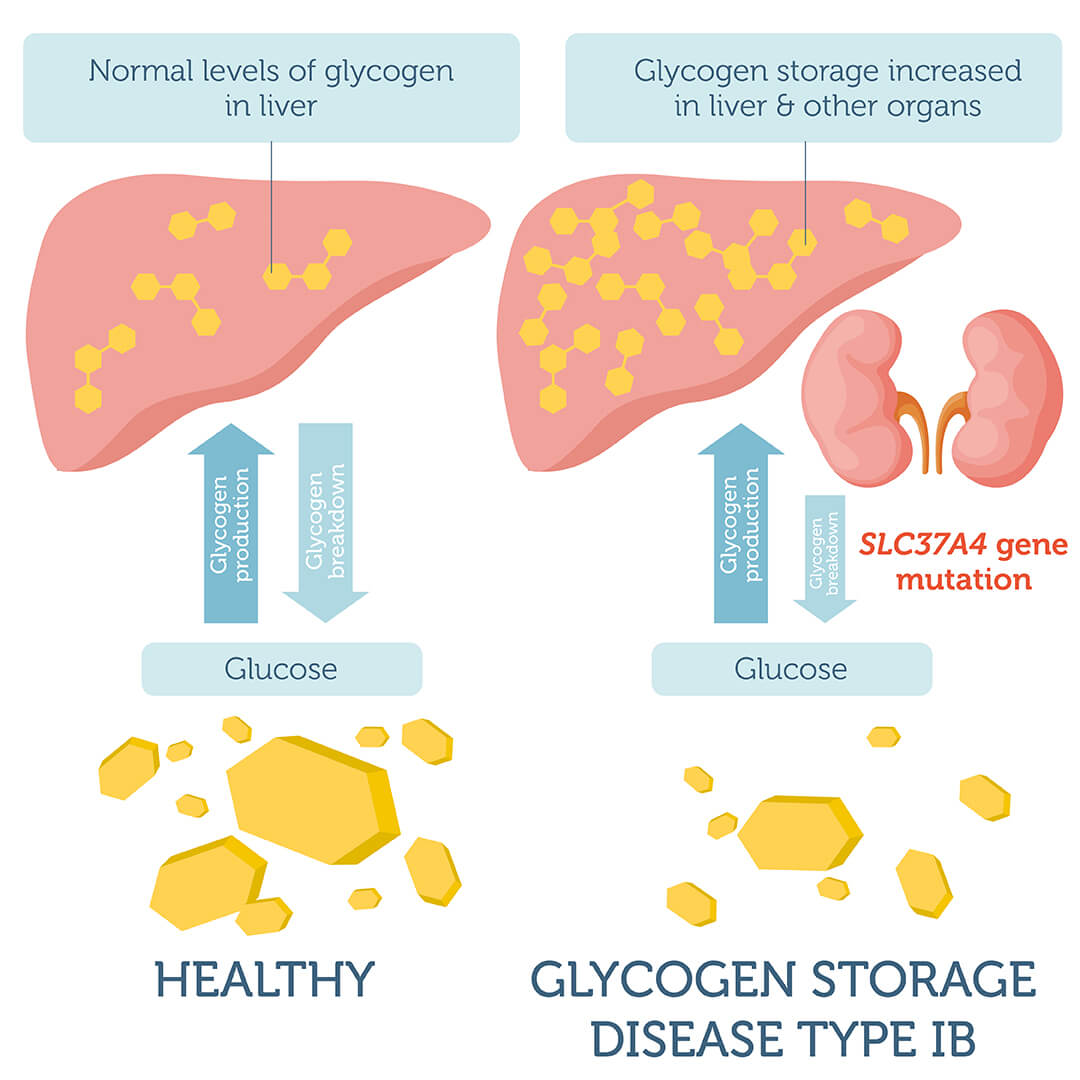
Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ib DNA Test DNA Access Lab

Medical Nutrition Therapy Diet Glycogen Storage Disease 1
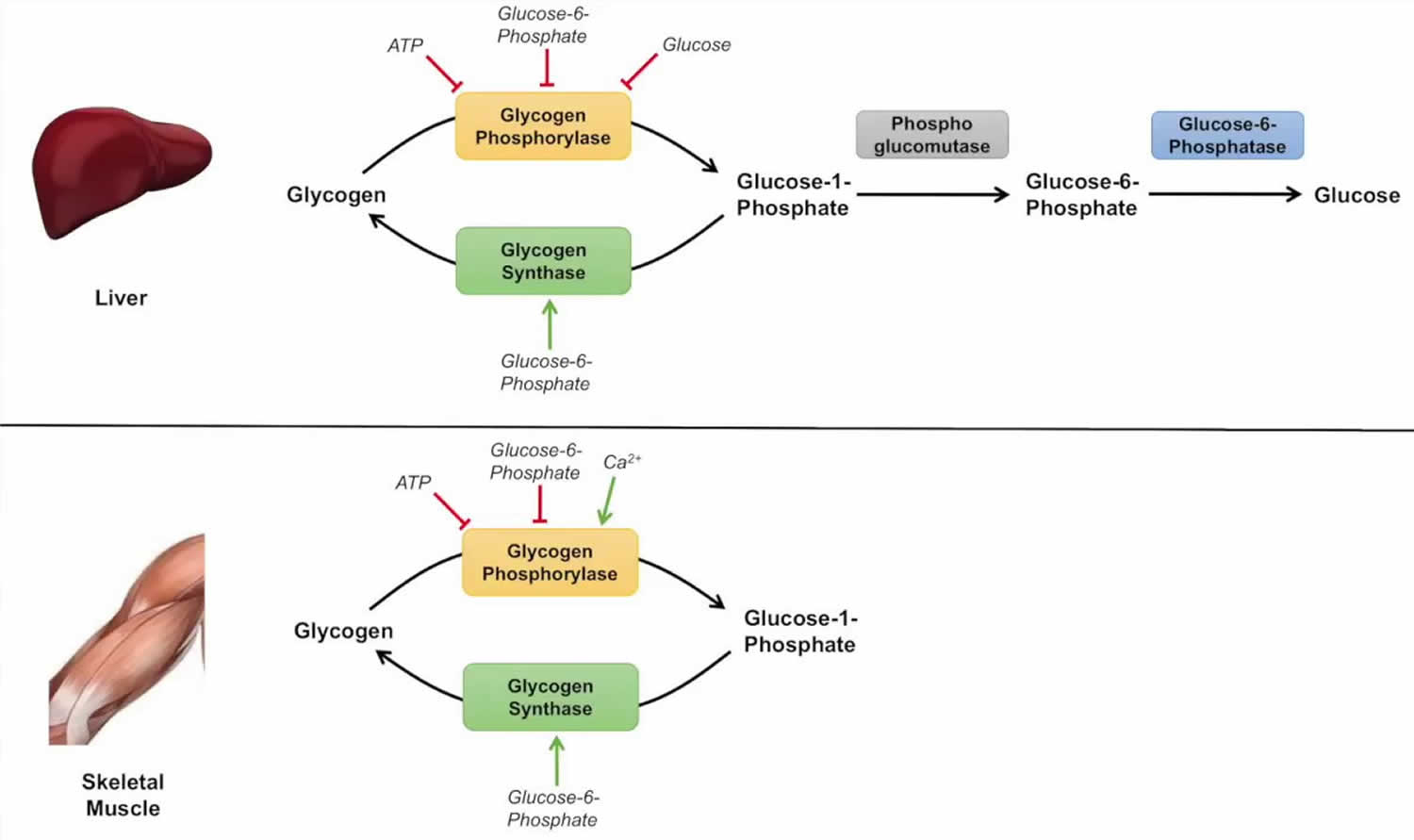
Glycogenolysis Definition Glycogenolysis Steps Pathway
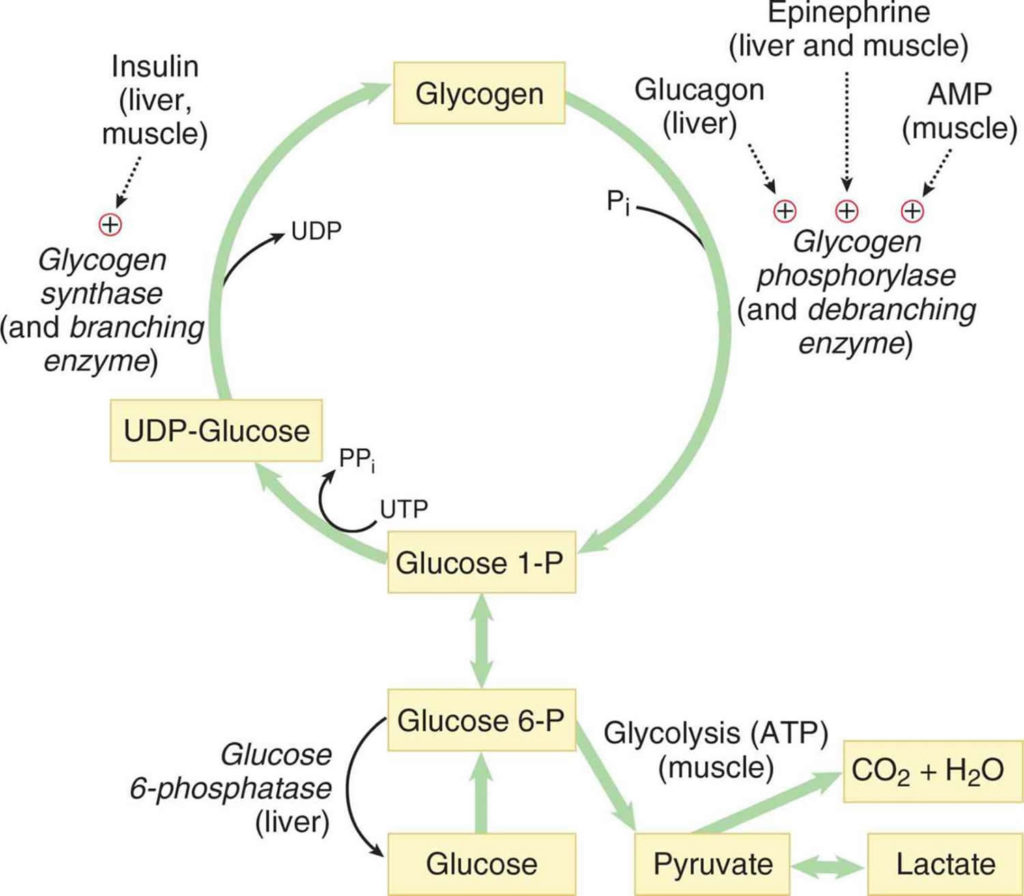
Glycogen Storage Disease Types Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Glycogen Storage Disease Type I

Glycogen Storage Disease Diet Is There A Diet Which Improves The

Glycogen Storage Disease Diet Is There A Diet Which Improves The
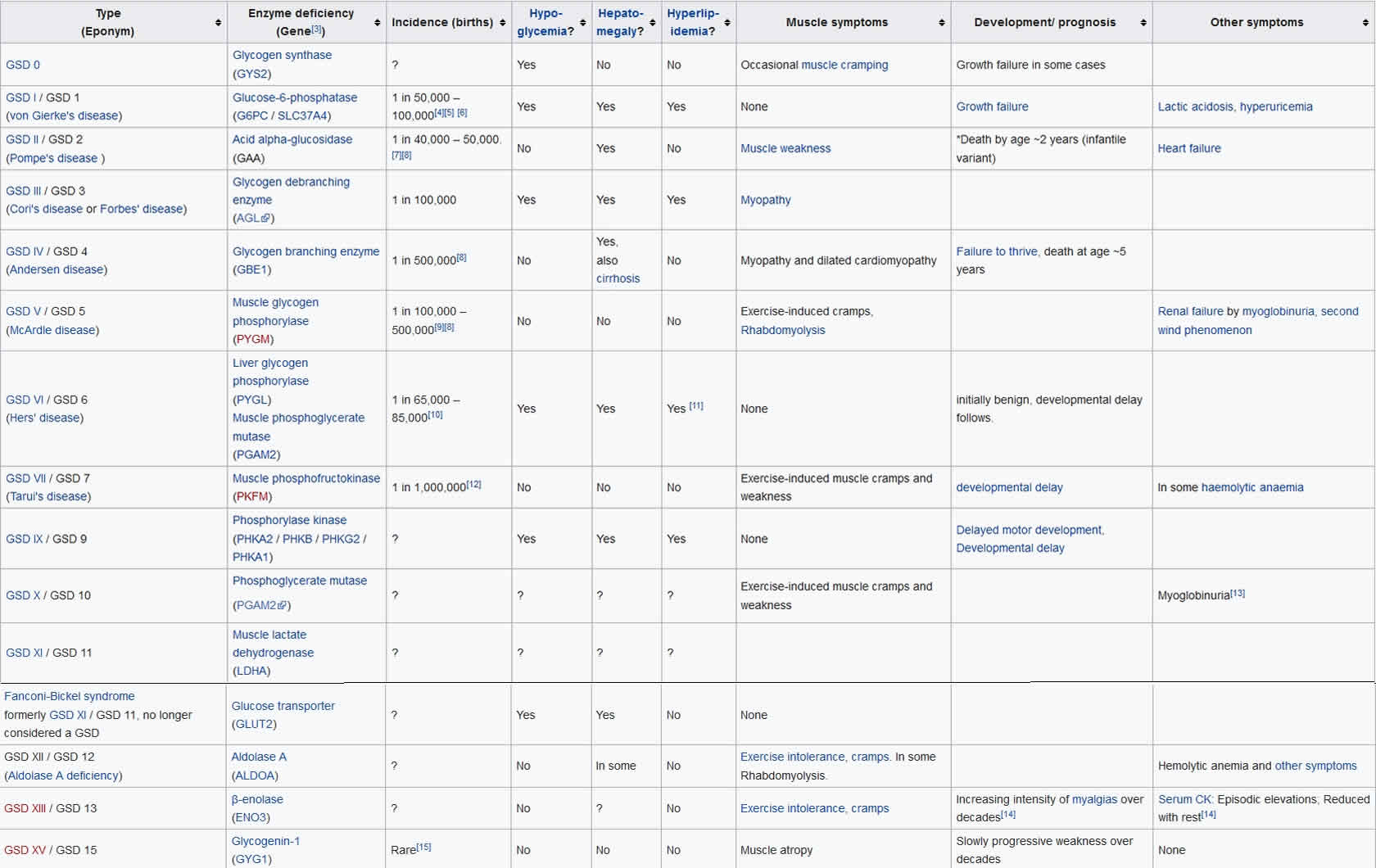
Glycogen Storage Disease Types Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Mnemonics Nursing School Notes Biochemistry

Glycogen Storage Disease Type I Video Anatomy Osmosis
Diet Plan For Glycogen Storage Disease - In glycogen storage diseases GSDs there is excessive glycogen build up in the muscle liver and or heart There are over 15 types of glycogen storage diseases which are mainly categorized by the type of tissue involved Types I III IV VI and IX primarily affect the liver Types II V and VII primarily affect the muscle