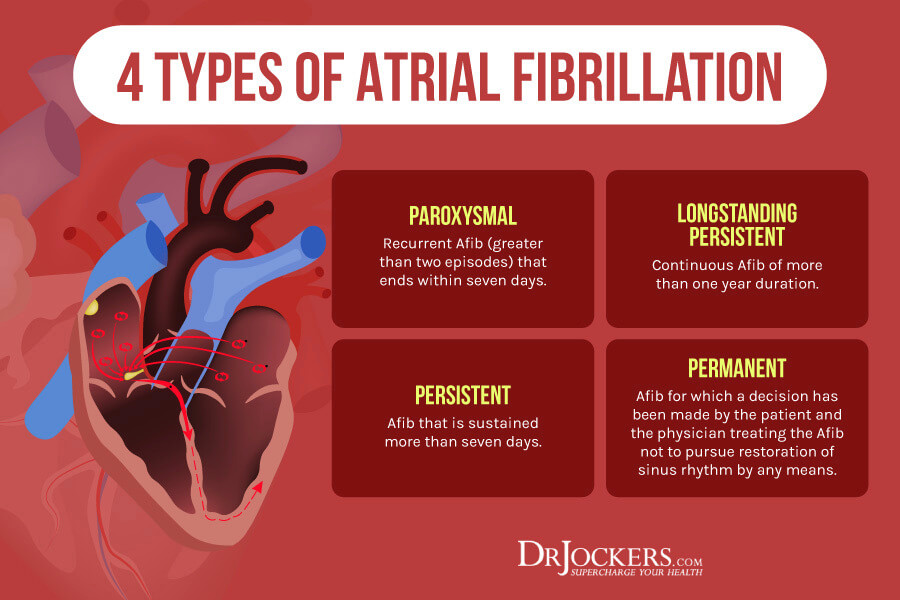
Diet Plan For Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia And Stage 3 Atrial fibrillation is the most commonly encountered cardiac arrhythmia in clinical practice box 1 7 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation PAF is intermittent episodes of atrial fibrillation that terminate within seven days either spontaneously or with intervention 8 This excludes atrial fibrillation that is triggered by transient causes such as
A heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute at rest is considered too fast and is a case of tachycardia The condition can be temporary or a more chronic issue stemming from heart disease or lifestyle choices Following a healthy AF is addressed in the 2014 ACC AHA HRS Guideline for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation 2014 AF guideline 10 The present guideline addresses other SVTs including regular narrow QRS complex tachycardias as well as other irregular SVTs eg atrial flutter with irregular ventricular response and multifocal atrial tachycardia MAT
Diet Plan For Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia And Stage 3
Diet Plan For Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia And Stage 3
https://cf.ppt-online.org/files/slide/t/TwyF4lSjhAvHf95zJGREKI6kZpBedcqbMVumLo/slide-22.jpg
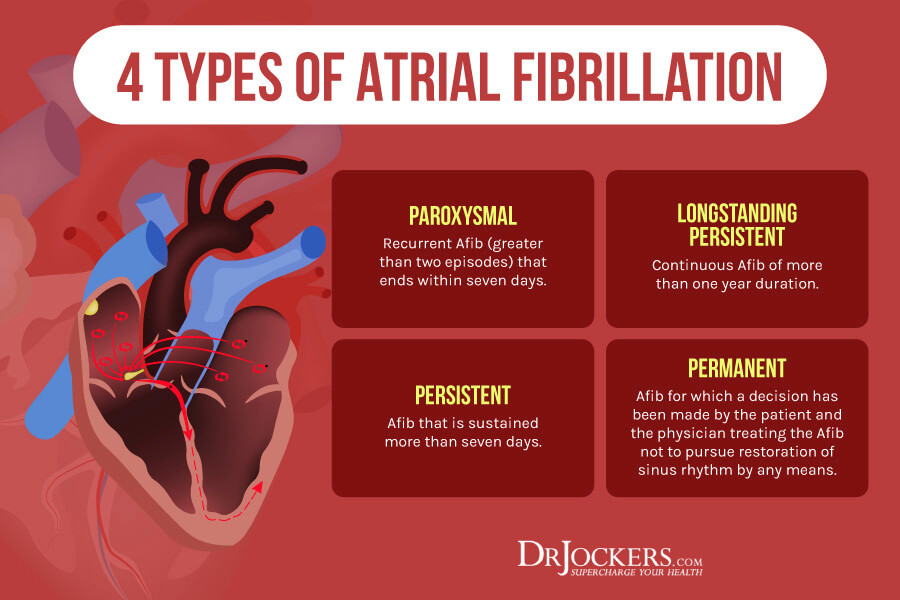
Types Of Afib Chart
https://drjockers.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Types-of-A-Fib.jpg

Atrial Fibrillation Diet A Beginner s 2 Week Guide On Managing AFib
https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51tTrFkrRoL._SL500_.jpg
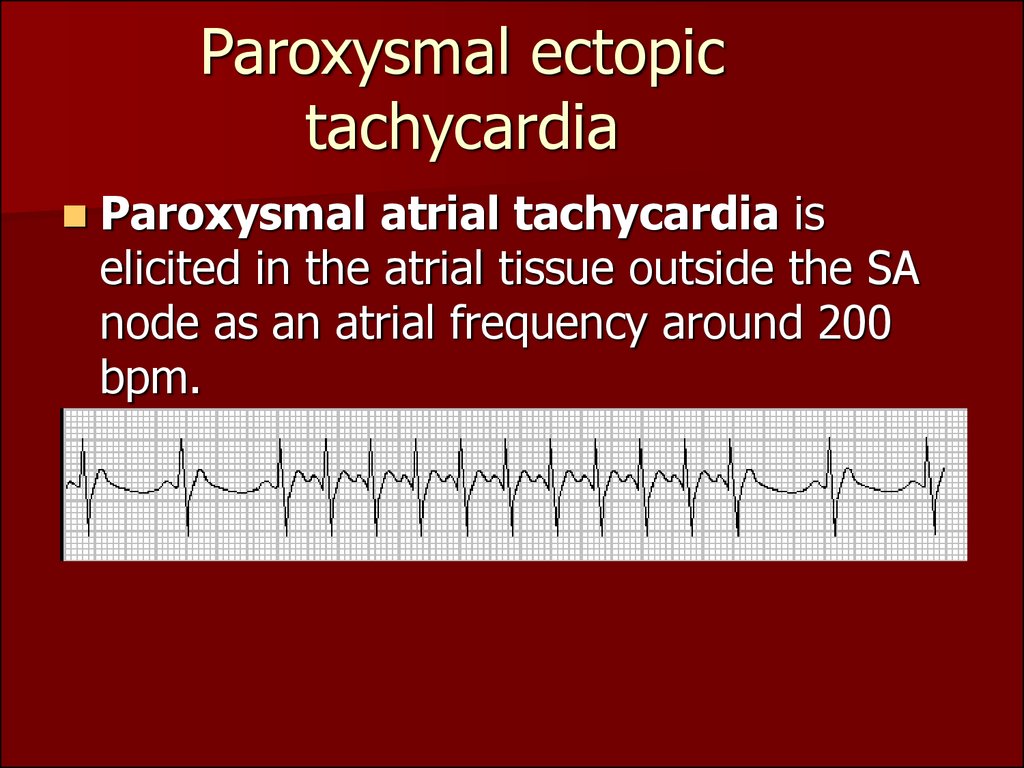
Atrial Tachycardia AT It is a regular atrial rhythm at a constant rate of 100 beats per minute bpm with discrete P waves and atrial activation sequences originating outside of the sinus node 1 The mechanism can be automaticity triggered activity or a microreentry circuit Focal ATs arise from a single discrete site within the left Atrial tachycardia is caused by a problem in the heart s conduction system which coordinates the heartbeat The issue in atrial tachycardia is the heart is beating too fast Patients can experience this event with or without symptoms Common symptoms include palpitations dizziness lightheadedness and passing out
Introduction Atrial tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia SVT usually seen in patients with structural heart abnormalities but can be seen in patients with structurally normal hearts Unlike other SVTs atrial tachycardia does not depend upon the atrioventricular junction or accessory pathways for initiation or maintenance Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia PAT is also known as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia PSVT PAT can cause an adult s heart rate to increase from between 60 and 100 beats per minute bpm
More picture related to Diet Plan For Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia And Stage 3
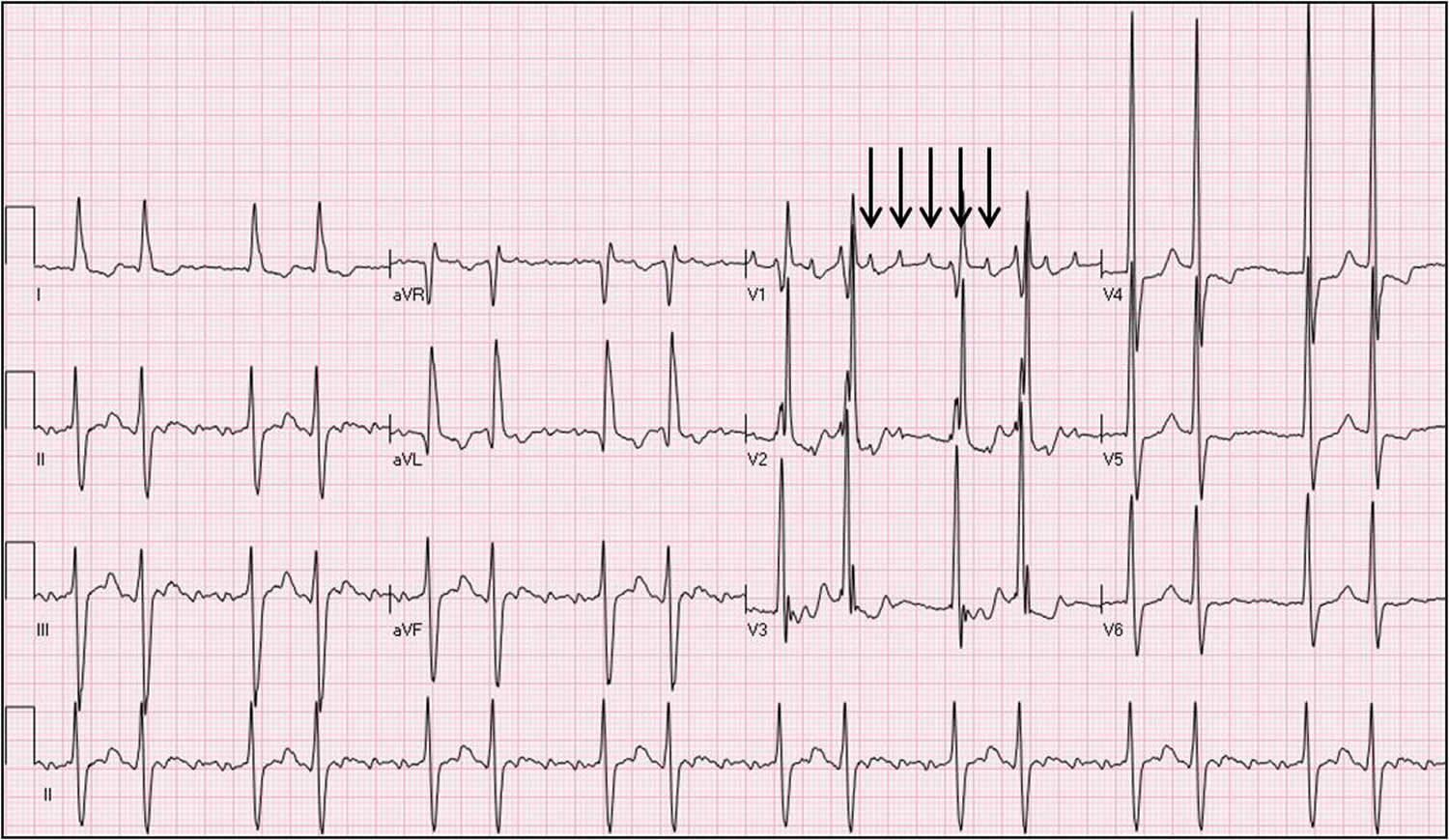
Atrial Tachycardia Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
https://healthjade.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/atrial-tachycardia_ecg.jpg

Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Heart Images And Photos Finder
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/90/94/a7/9094a71f1f19bfae22ebb0d91e12cc7a.jpg
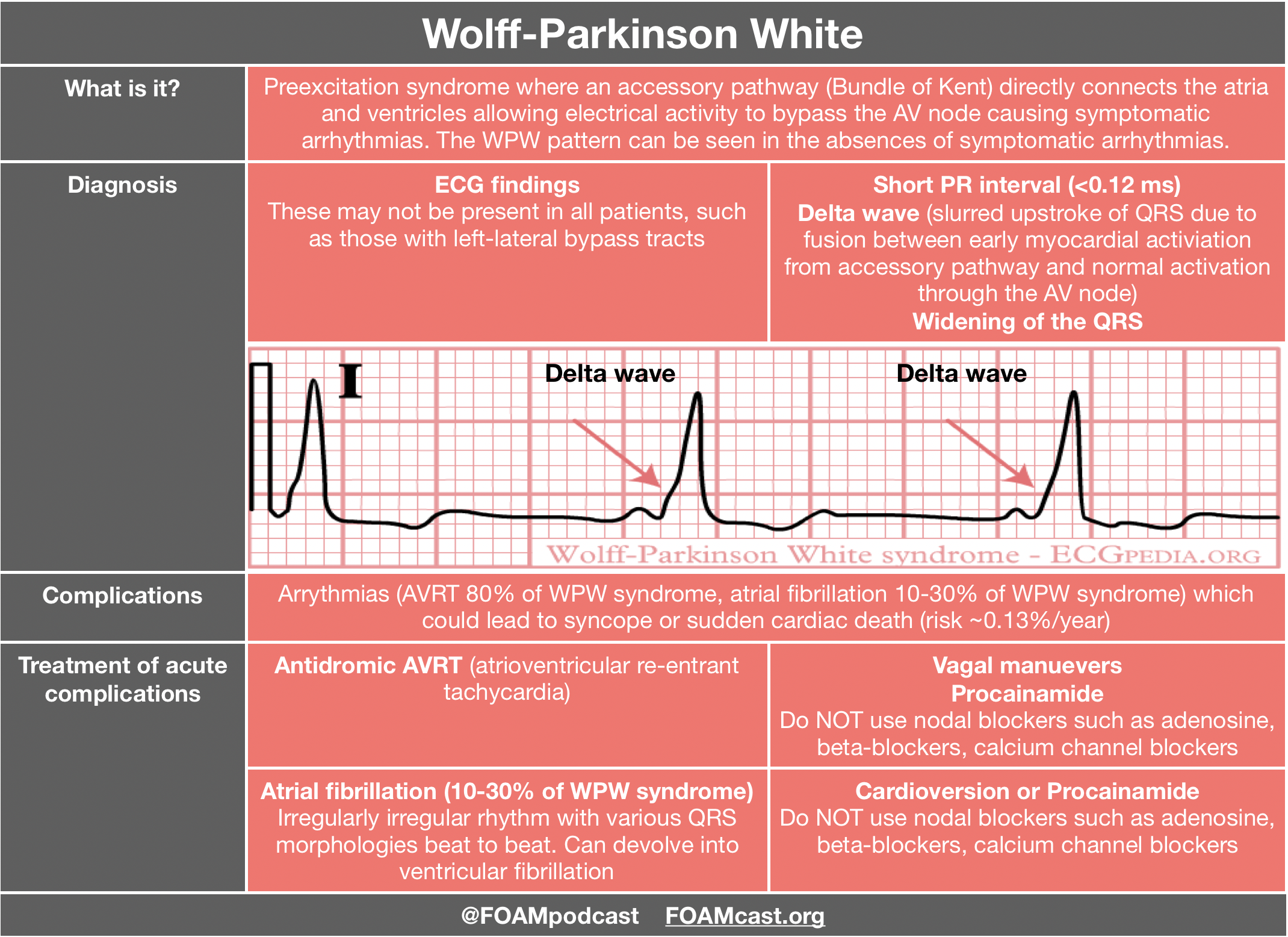
Supraventricular Tachycardia Treatment FOAMcast
http://foamcast.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Screen-Shot-2019-02-18-at-3.00.05-AM.png
Sustained tachycardia A sustained tachycardia more than 30 seconds is usually symptomatic and significant ventricular or supraventricular Symptoms such as diaphoresis dizziness or even syncope might appear as a manifestation of a low cardiac output due to the short diastolic intervals If not treated promptly sustained arrhythmias Patients with previous paroxysmal atrial fibrillation AF who follow a Mediterranean diet enriched with extra virgin olive oil after a catheter ablation procedure saw improved clinical outcomes when compared to those who freely selected their diet research presented at the Heart Rhythm Society HRS annual meeting 16 19 May
atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia AVRT atrial tachycardia AT and a few more tachyarrhythmias 2 Ac el ra td hym sn b ifg op u VNRT most common type of paroxysmal SVT followed by AVRT 3 For patients presenting with PSVT a 12 lead electrocardiogram ECG showing a narrow complex tachycardia is the basis for Patients at high risk for tachycardia may need education on lifestyle changes such as weight loss quitting smoking substance abuse treatment limiting caffeine and eating a heart healthy diet 4 Administer antiarrhythmics Beta blockers calcium channel blockers digoxin and more slow electrical heart impulses
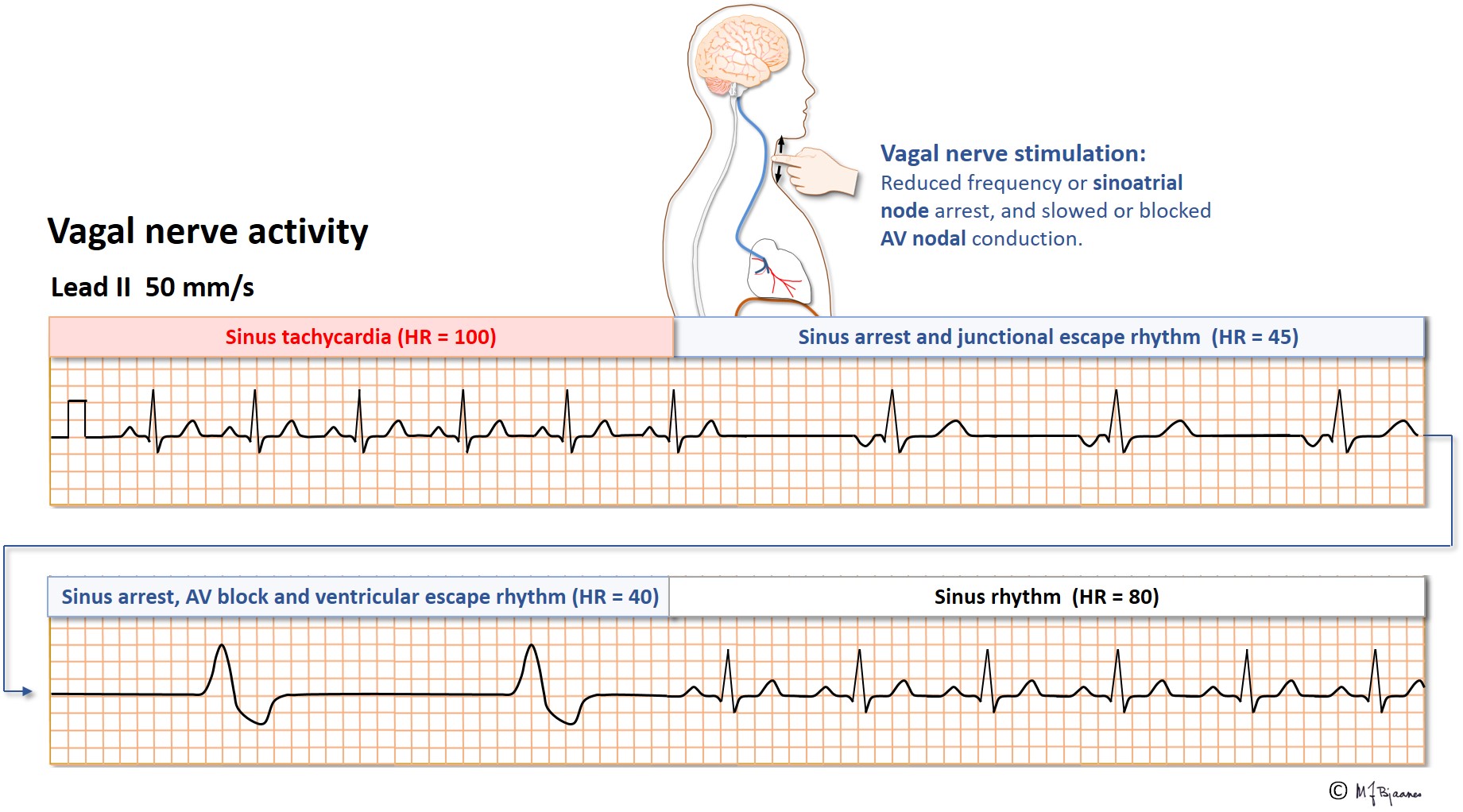
Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia
https://studmed.uio.no/elaring/fag/hjertesykdommer/en/ecg/images/4/fig01b.jpg

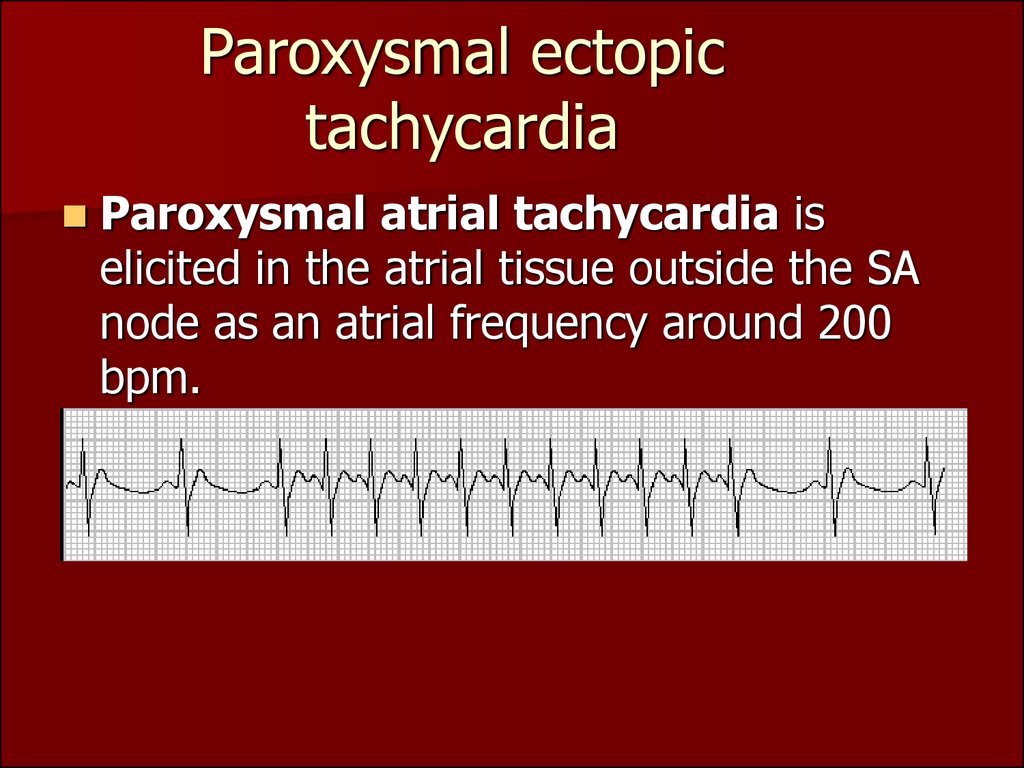
Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia
https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/57da631bee13e8266e85d630e742b5cfe23c7226/2-Figure1-1.png
https://www.bmj.com/content/375/bmj-2021-058568
Atrial fibrillation is the most commonly encountered cardiac arrhythmia in clinical practice box 1 7 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation PAF is intermittent episodes of atrial fibrillation that terminate within seven days either spontaneously or with intervention 8 This excludes atrial fibrillation that is triggered by transient causes such as
https://www.livestrong.com/article/471800-diet-for-people-with-tach…
A heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute at rest is considered too fast and is a case of tachycardia The condition can be temporary or a more chronic issue stemming from heart disease or lifestyle choices Following a healthy

Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia

Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia

Study Plan AT Atrial Tachycardia AF Atrial Flutter AFib Atrial
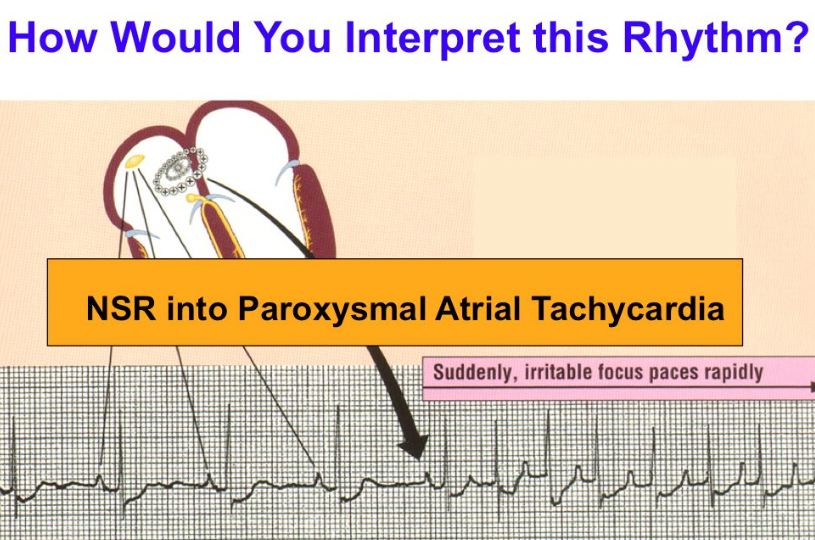
Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia

Pin On Relax
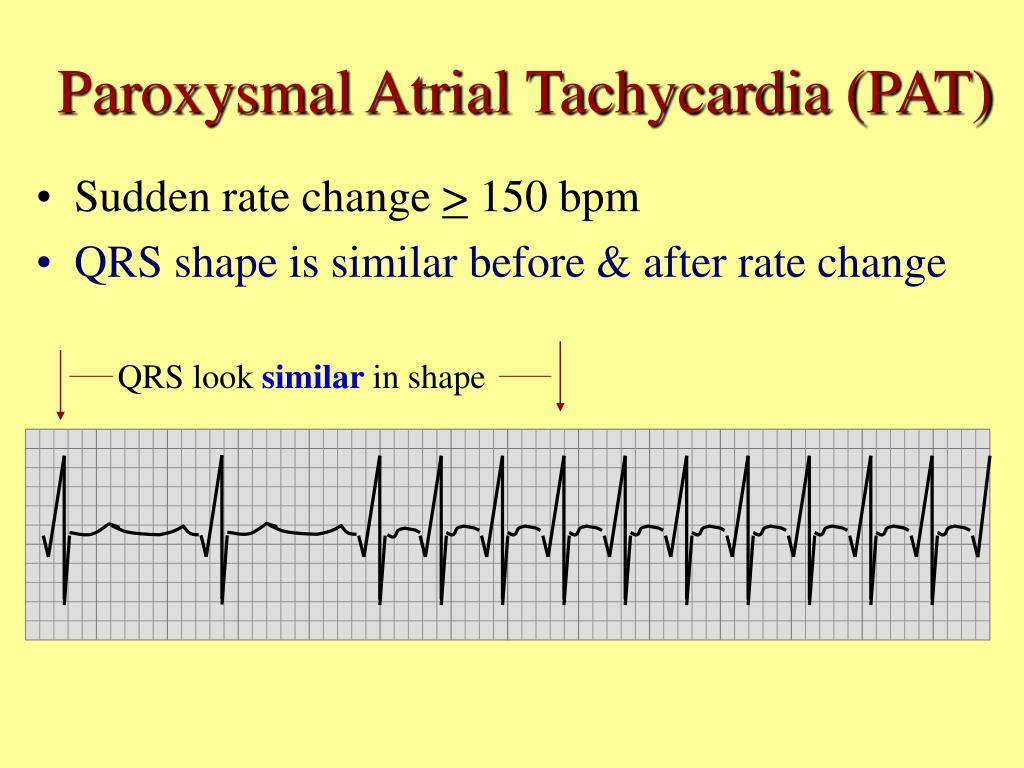
Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia

Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia

Understanding Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia PAT
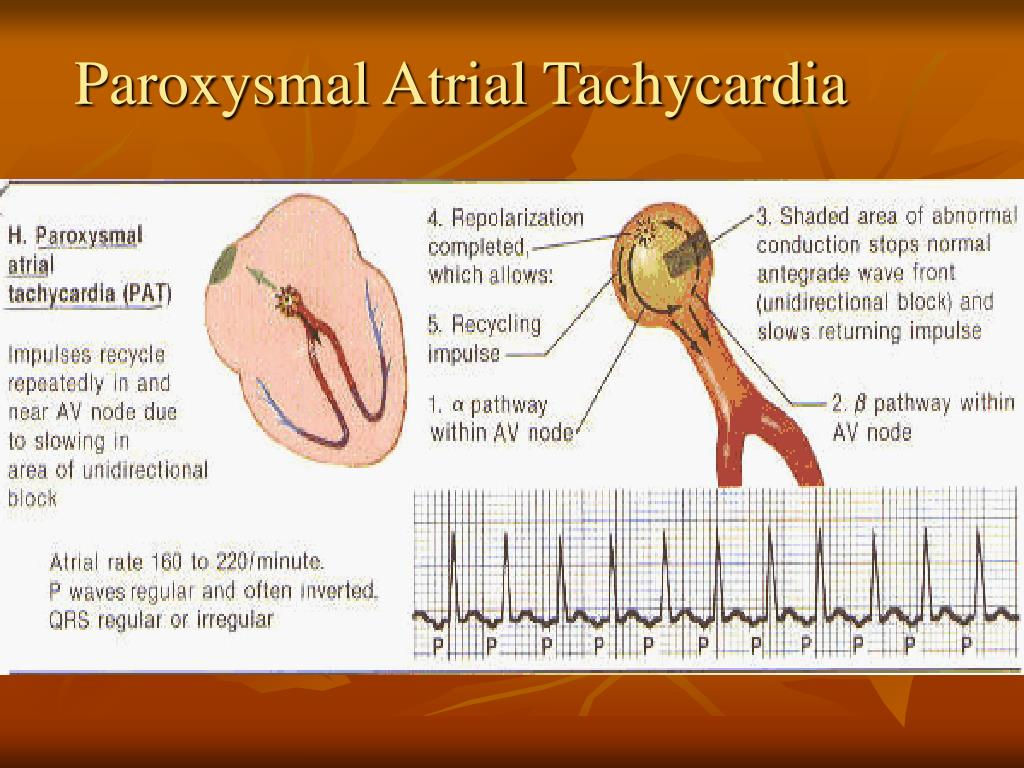
PPT DIAGNOSIS OF CARDIAC RHYTHMS PowerPoint Presentation Free

Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia
Diet Plan For Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia And Stage 3 - Introduction Atrial tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia SVT usually seen in patients with structural heart abnormalities but can be seen in patients with structurally normal hearts Unlike other SVTs atrial tachycardia does not depend upon the atrioventricular junction or accessory pathways for initiation or maintenance