Inspiration And Expiration Chest Size The intercostal muscles contract and move the ribs upwards and outwards This increases the size of the chest and decreases the air pressure inside it which sucks air into the lungs
Results The breathing with mainly inspiration group BMIG showed significant differences in chest size during inspiration CSI chest expansion values CEVs forced vital capacity One common condition is a flail chest resulting from trauma where there are multiple rib fractures causing a segment of the thoracic wall to move paradoxically Basically the affected portion of the wall moves inwards
Inspiration And Expiration Chest Size

Inspiration And Expiration Chest Size
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/2rNW6Y_tNuc/maxresdefault.jpg

Pressure Volume Relationships Normal Inspiration And Expiration YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vvs5jePHuvA/maxresdefault.jpg

05I Pulmonary Ventilation And Inspiration And Expiration YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/D5Ofb3Hwz8E/maxresdefault.jpg
Chest expansion score which represents the circumference magnitude of the thoracic cage is used for a target when treating patients with respiratory disease It represents a scan performed with the patient on supine and images obtained at the end expiration It is a useful method for detecting small airways obstructive lung disease
The diaphragm and external intercostals mediate inspiration and expiration by contracting or relaxing During inspiration the external intercostals and the diaphragm contract expanding the chest wall From a physiological standpoint the lung volumes are either dynamic or static Both subclasses are measured at different degrees of inspiration or expiration however dynamic lung volumes
More picture related to Inspiration And Expiration Chest Size

VENTILATION INSPIRATION VS EXPIRATION MECHANISM OF BREATHING YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/brIR-w9bygU/maxresdefault.jpg

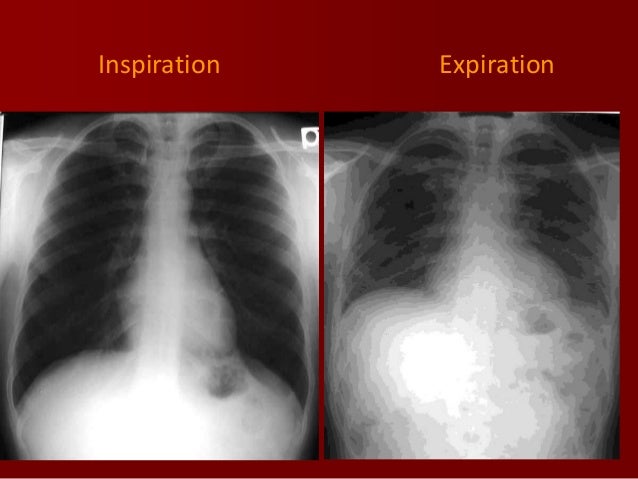
BASICS OF CHEST X RAY PART3 INSPIRATION VS EXPIRATION QUALITY OF X RAY
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/l-S2pawrs08/maxresdefault.jpg
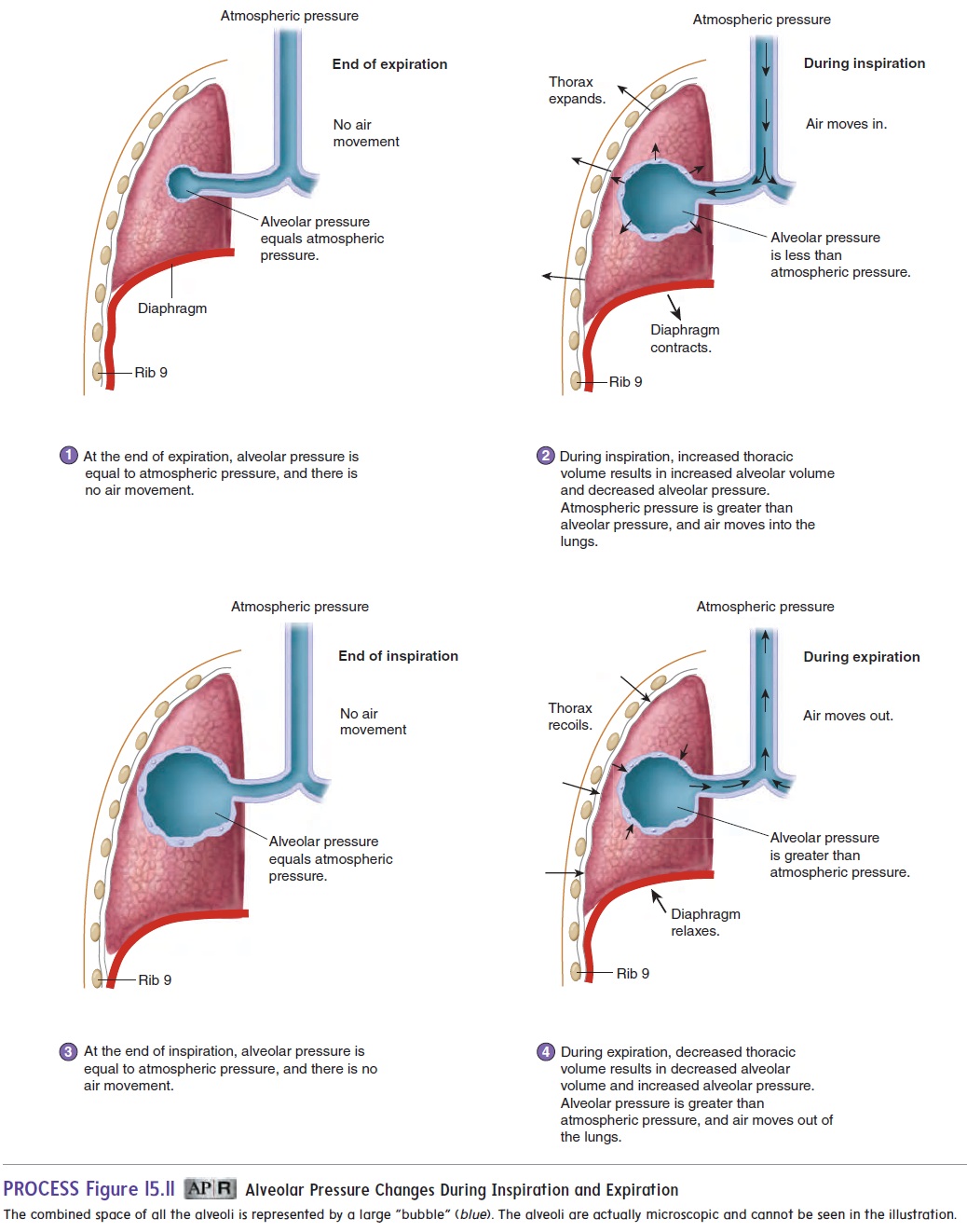
Changing Thoracic Volume
https://img.brainkart.com/imagebk22/UD0UvPw.jpg
Results The breathing with mainly inspiration group BMIG showed significant differences in chest size during inspiration CSI chest expansion values CEVs forced vital Pulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps inspiration and expiration Inspiration is the process that causes air to enter the lungs and expiration is the process that causes air to leave the lungs Figure 22 3 3 A respiratory cycle
This may result from a poor inspiratory effort or any other condition that prevents full inspiration This patient s chest x ray is normal in full inspiration In relative expiration the cardiac Results The breathing with mainly inspiration group BMIG showed significant differences in chest size during inspiration CSI chest expansion values CEVs forced vital capacity

Anatomy Physiology Flashcards Quizlet
https://o.quizlet.com/5ieRE35Fv2q0AYKoZAVjJA.jpg

Inspiration And Expiration Respiratory System Human Anatomy And
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/b5/a0/5d/b5a05da39f8f098260059cc604aa2887.jpg

https://www.bbc.co.uk › bitesize › guides
The intercostal muscles contract and move the ribs upwards and outwards This increases the size of the chest and decreases the air pressure inside it which sucks air into the lungs

https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › articles
Results The breathing with mainly inspiration group BMIG showed significant differences in chest size during inspiration CSI chest expansion values CEVs forced vital capacity

Average Chest Circumference cm S D Download Table

Anatomy Physiology Flashcards Quizlet

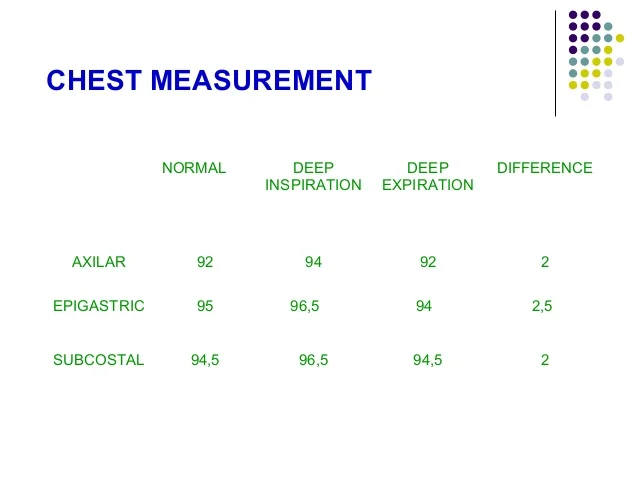
Chest Measurement
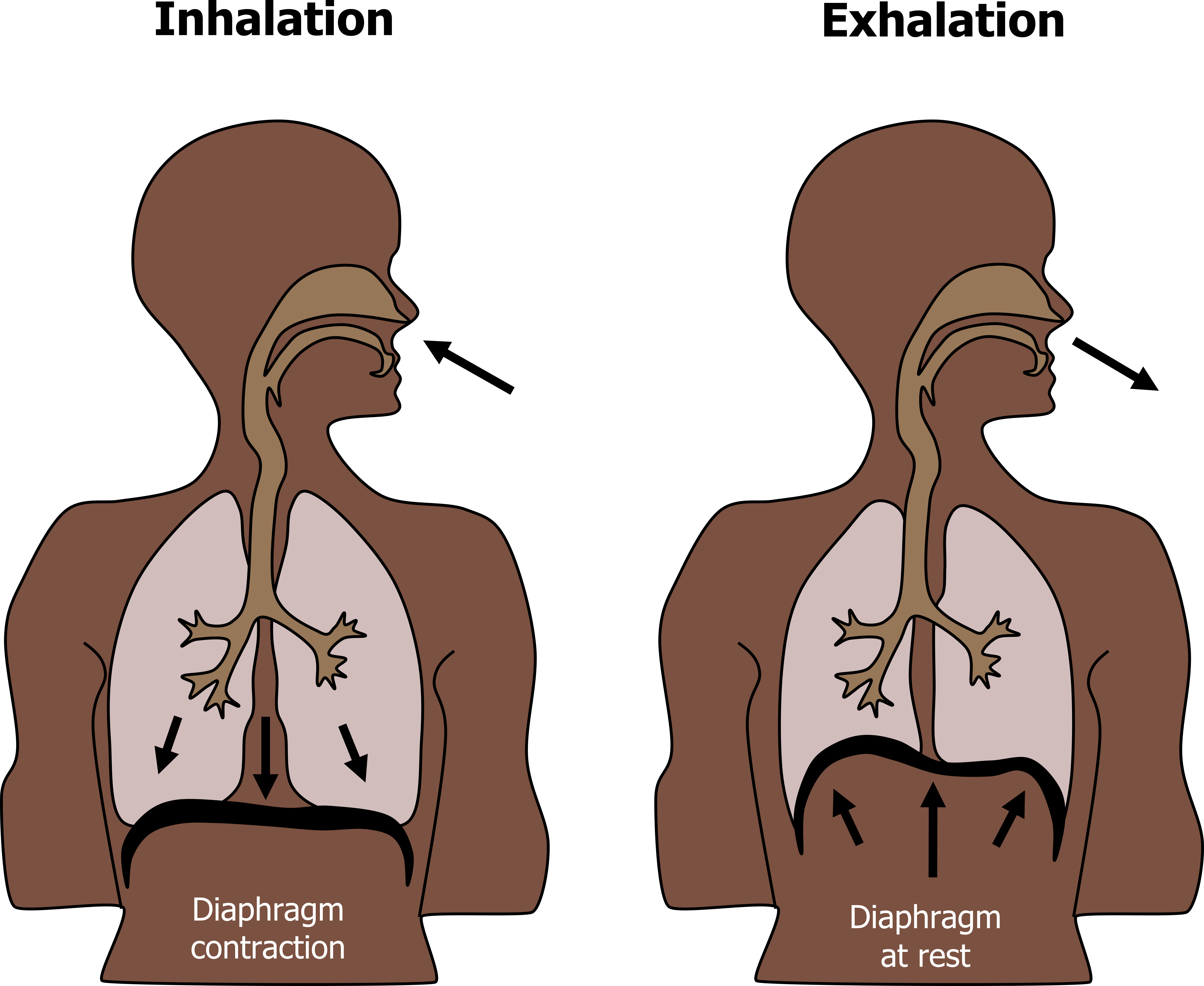
Diaphragm Contraction
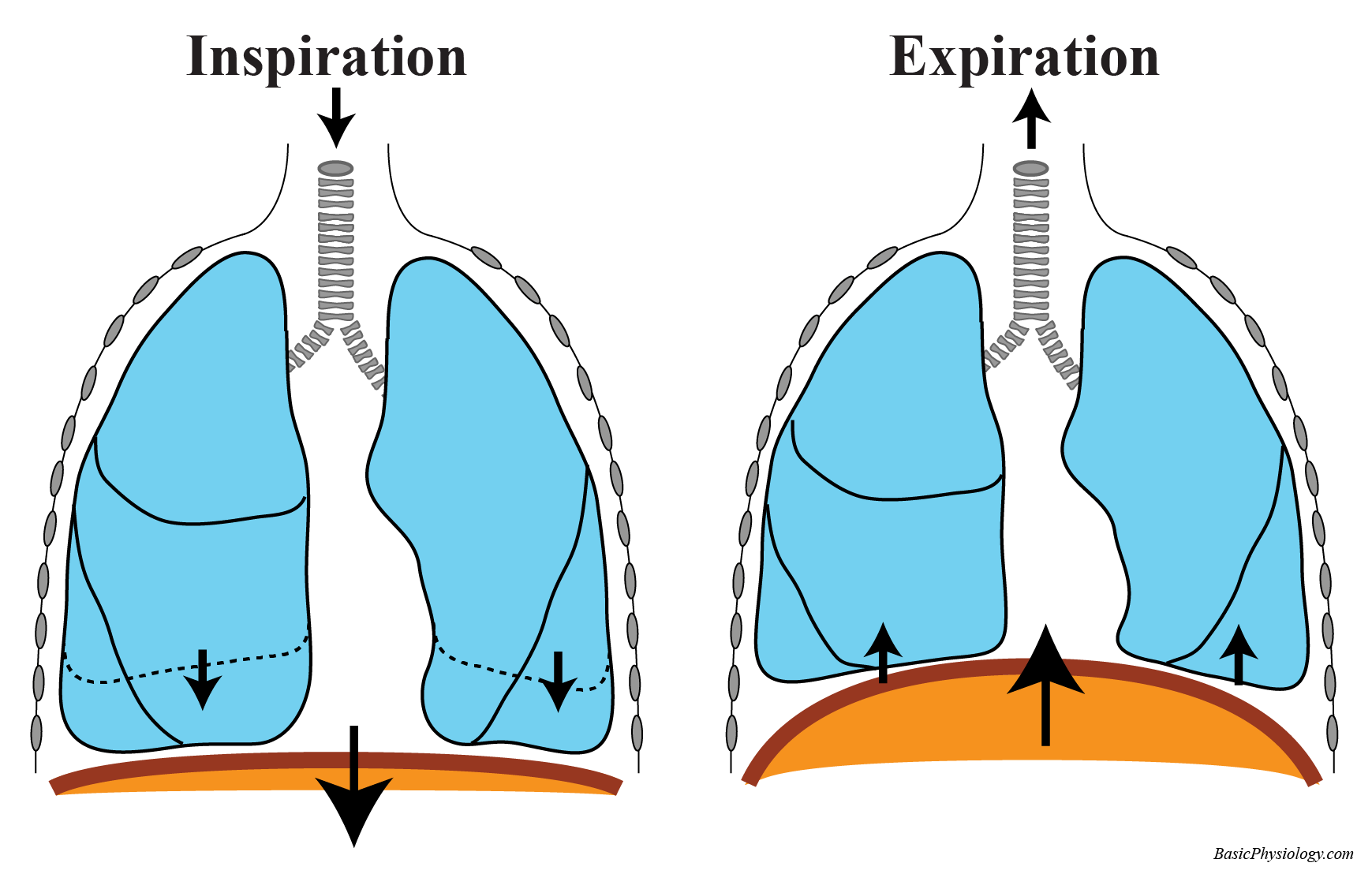
Dysfunctional Breathing Asthma Foundation NZ
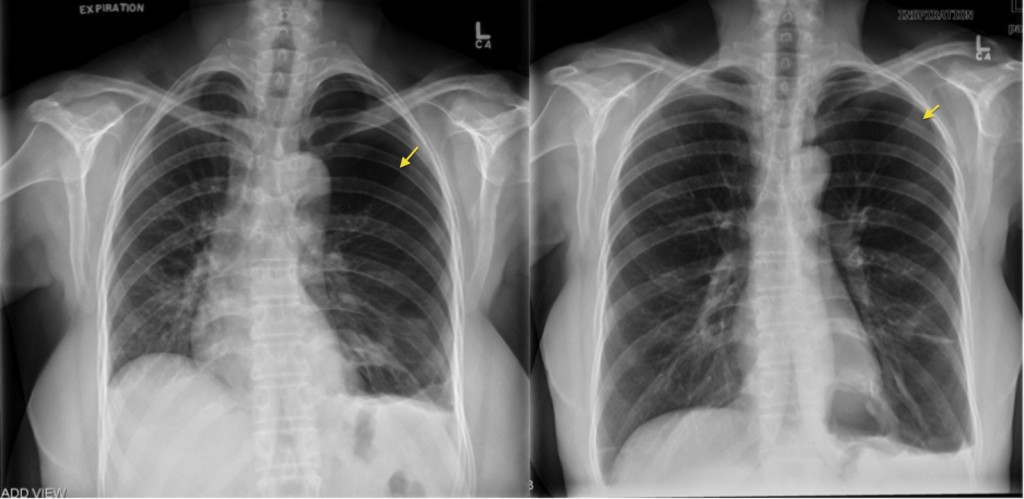
Pneumothorax Expiration Radiology At St Vincent s University Hospital

Pneumothorax Expiration Radiology At St Vincent s University Hospital
Parkinson Study Case

RADT 1330 Chap 2 Chest Lesson 2 Flashcards Quizlet
Chest X Ray
Inspiration And Expiration Chest Size - The diaphragm and external intercostals mediate inspiration and expiration by contracting or relaxing During inspiration the external intercostals and the diaphragm contract expanding the chest wall