Rabies Vaccination In Germany WHO fact sheet on rabies providing key facts and information on symptoms diagnosis transmission post exposure prophylaxis local treatment prevention WHO response
Rabies is a viral disease transmitted from mammals to humans that causes an acute encephalitis There are two clinical manifestations of rabies furious and paralytic Furious rabies is the most Rabies is an infectious viral disease that is almost always fatal following the onset of clinical signs It affects domestic and wild animals and is spread to people through bites or scratches
Rabies Vaccination In Germany

Rabies Vaccination In Germany
https://www.petmd.com/sites/default/files/DogVaccinations-PetMD-R2.png
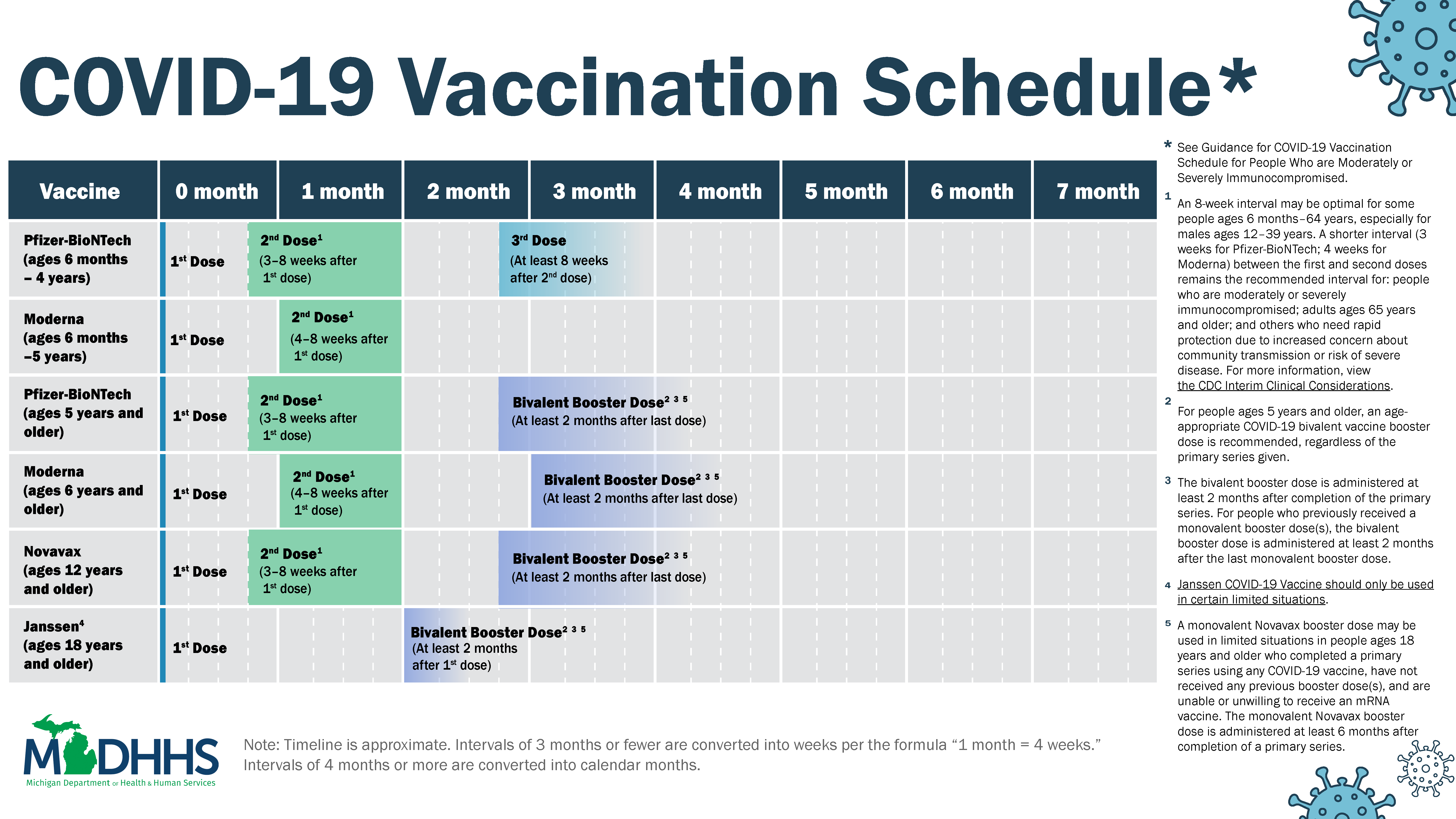
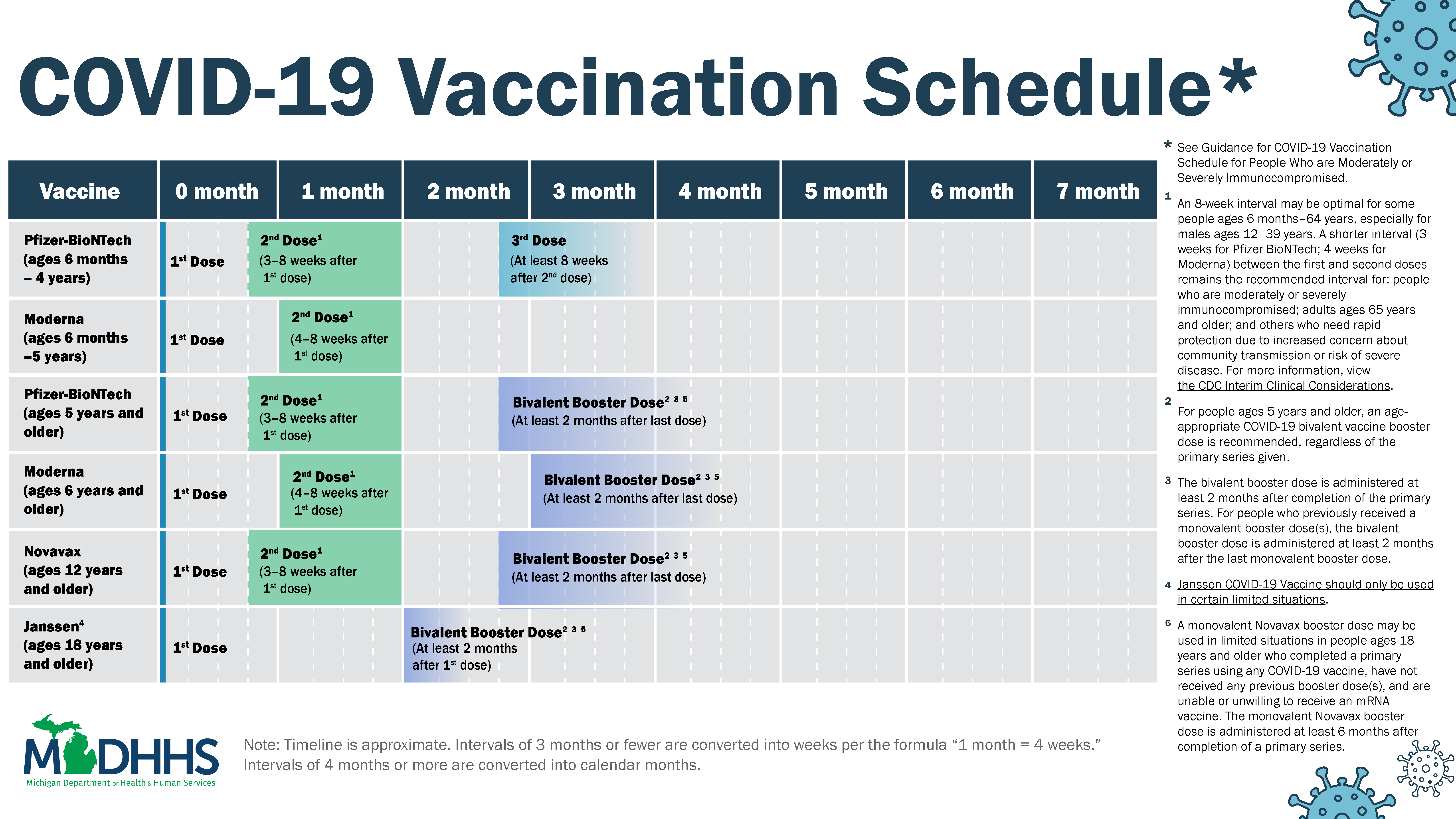
COVID 19 COVID 19 Vaccine Central Macomb County
https://www.michigan.gov/coronavirus/-/media/Project/Websites/coronavirus/Folder2/COVID-19-Vaccination-Schedule_10-13-22_v2.jpg?rev=841a13959d1441d4926fa62119d312bc

DA C Luzon Logs Fewer Rabies infected Humans Pets Philippine News
https://files01.pna.gov.ph/ograph/2023/10/03/anti-rabies-vaccination-central-luzon.jpg
United Against Rabies to achieve Zero by 30 WHO Food and Agriculture organization World Organisation for Animal Health and Global Alliance for Rabies have Rabies viruses belong to the genus Lyssavirus of the Rhabdoviridae family Rabies is a zoonosis transmission from animals to humans and human infection usually occurs following a bite or
Rabies is preventable through three proven effective interventions Awareness of rabies disease engages communities and empowers people to save themselves by seeking Rabies is a vaccine preventable zoonotic viral disease Dogs are the source of the vast majority of rabies virus transmission through bites or scratches usually via saliva
More picture related to Rabies Vaccination In Germany

Rabies Transmission
https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/uploads/new_news_image/Key_Facts_Regarding_Rabies.jpg

News And Releases Pasig City
https://assets.pasigcity.gov.ph/storage/news/2025/05/05/68186e52ced5d1746431570495018464-716969817345859-3456893504486312863-n.jpg
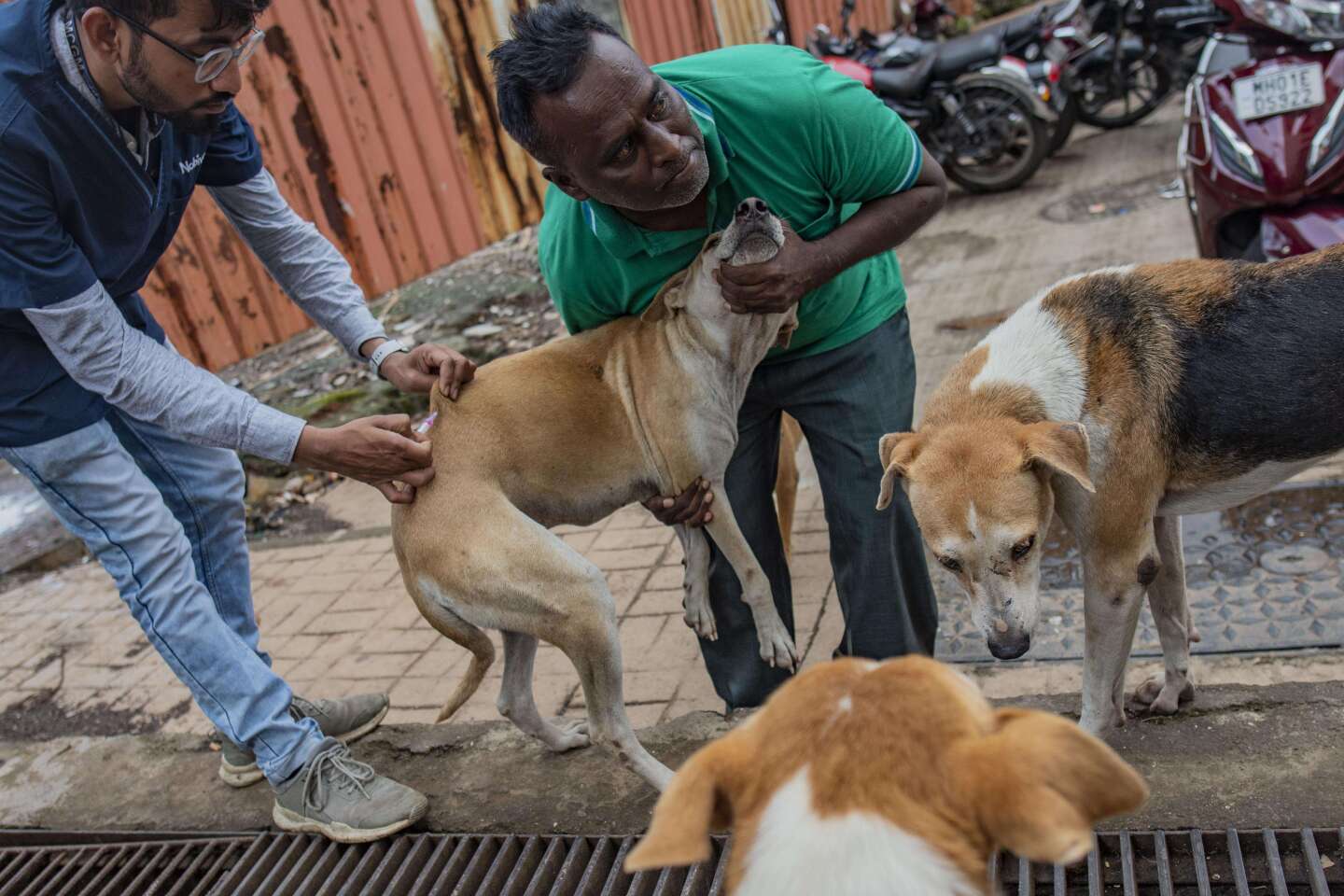

Dog With Rabies
https://img.lemde.fr/2023/05/18/0/21/4965/3310/1440/960/60/0/3208462_1684420508426-sipa-shutterstock41007051-000001.jpg
Human rabies is a 100 vaccine preventable disease yet it continues to kill Rabies vaccinations are highly effective safe and well tolerated The WHO recommends 2 Rabies Rabies in Viet Nam Rabies is an infectious viral disease that is almost always fatal following the onset of clinical symptoms In up to 99 of cases domestic dogs
[desc-10] [desc-11]
Rabies And Bite Reporting Maricopa County AZ
https://www.maricopa.gov/ImageRepository/Document?documentID=6646
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rabies-overview-4156466_final-8c26e268da134ff1b2c08160d68f42c4.png)
Was Ist Tollwut MedDe
https://www.verywellhealth.com/thmb/wP8DUw0FkH0E5UysUPvDbeKYwEU=/1500x0/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rabies-overview-4156466_final-8c26e268da134ff1b2c08160d68f42c4.png

https://www.who.int › news-room › fact-sheets › detail › rabies
WHO fact sheet on rabies providing key facts and information on symptoms diagnosis transmission post exposure prophylaxis local treatment prevention WHO response
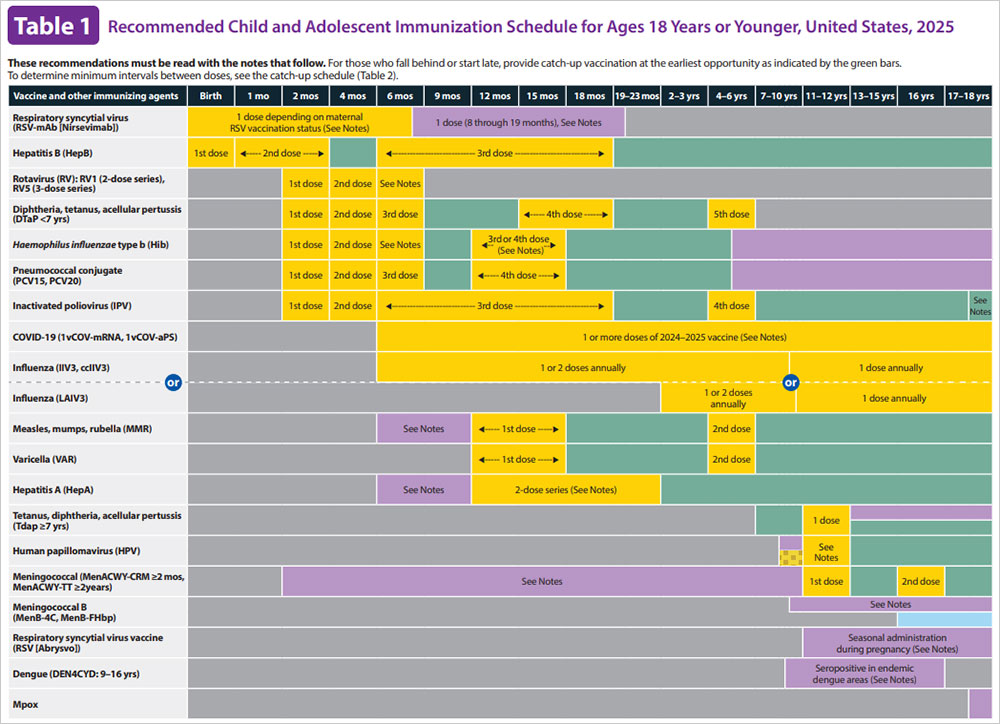
https://www.who.int › docs › default-source › ntds › rabies …
Rabies is a viral disease transmitted from mammals to humans that causes an acute encephalitis There are two clinical manifestations of rabies furious and paralytic Furious rabies is the most

Covid Sertifikats
Rabies And Bite Reporting Maricopa County AZ

Rabies Vaccine Certificate Template

Rabies Infected Bite

Free Rabies Vaccine Cook County IL Offering Residents Free Rabies

Free Rabies Vaccine Cook County IL Offering Residents Free Rabies
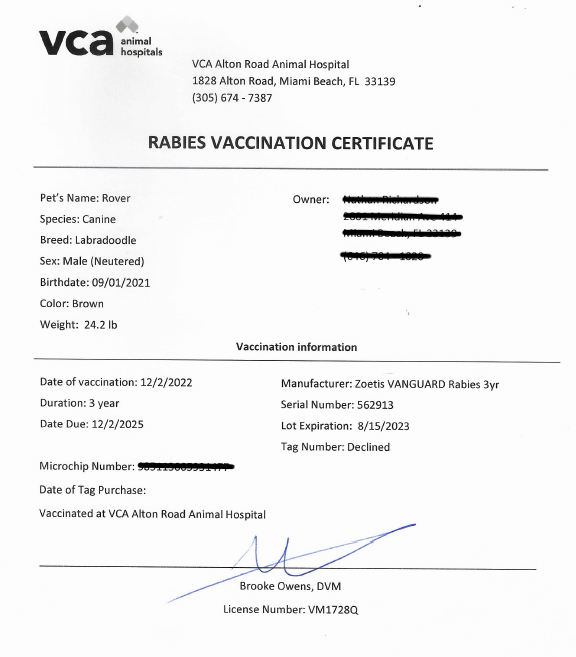
What Are The Rabies Vaccination Certificate Requirements

Successful 2016 Oral Rabies Vaccination Campaign Completed THE

Our Spay Neuter animal Saipan Cares For Animals CNMI Facebook
Rabies Vaccination In Germany - Rabies viruses belong to the genus Lyssavirus of the Rhabdoviridae family Rabies is a zoonosis transmission from animals to humans and human infection usually occurs following a bite or