What Is Rigid Body The rigid body motion can be expressed as When a constraint is expressed by equalities it is termed as holonomic constraint and those who do not are called non holonomic constraints Again if the constraint is independent of time it is called scleronomic constraints and if it is dependent of time explicitly then it is called rheonomic
Rigid body is a body that does not get deformed or change its shape even due to the action of any external forces or loads In case of Rigid body the distance remains constant between any of the two points when the rigid body is under the action of loads A planar rigid body has 3 DOF degrees of freedom in the absence of any constraints while a spatial rigid body has 6 DOF three translations and three rotations The amount of DOF that is available for the bodies to move freely is therefore decreased by the amount of DOF that the joint permits when a joint is added between two rigid bodies
What Is Rigid Body

What Is Rigid Body
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/1z013iS8MkU/maxresdefault.jpg

EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY PART 01 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/doY2MIsU2aQ/maxresdefault.jpg

Rigid Body Physics For Beginners Blender Tutorial YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/lctjzasiy64/maxresdefault.jpg
A rigid body rotates about a fixed axis with a variable angular speed in rad sec at any time t in seconds angular speed 3 5t rad sec To find The angle through which it rotates before coming to rest Formula required The Formula for instantaneous angular velocity d d t A system of two bodies of masses m and M being interconnected by a spring of stiffness k in its natural length moves towards a rigid wall on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in figure with a K E of system E
a Two equal and opposite forces acting on a rigid body such that their lines of action don t coincide constitute a couple This couple produces the turning effect on the body Hence the rigid body will rotate b If the two equal and opposite forces act in such a way that their lines of action coincide then the body will not rotate A rigid body has translational as well as rotational motion If a force couple is applied on the object then which of the following quantities remains unchanged due to the force couple 1 Rotational kinetic energy 2 Translation kinetic energy 3 Total kinetic energy 4 Angular momentum about centre of mass
More picture related to What Is Rigid Body
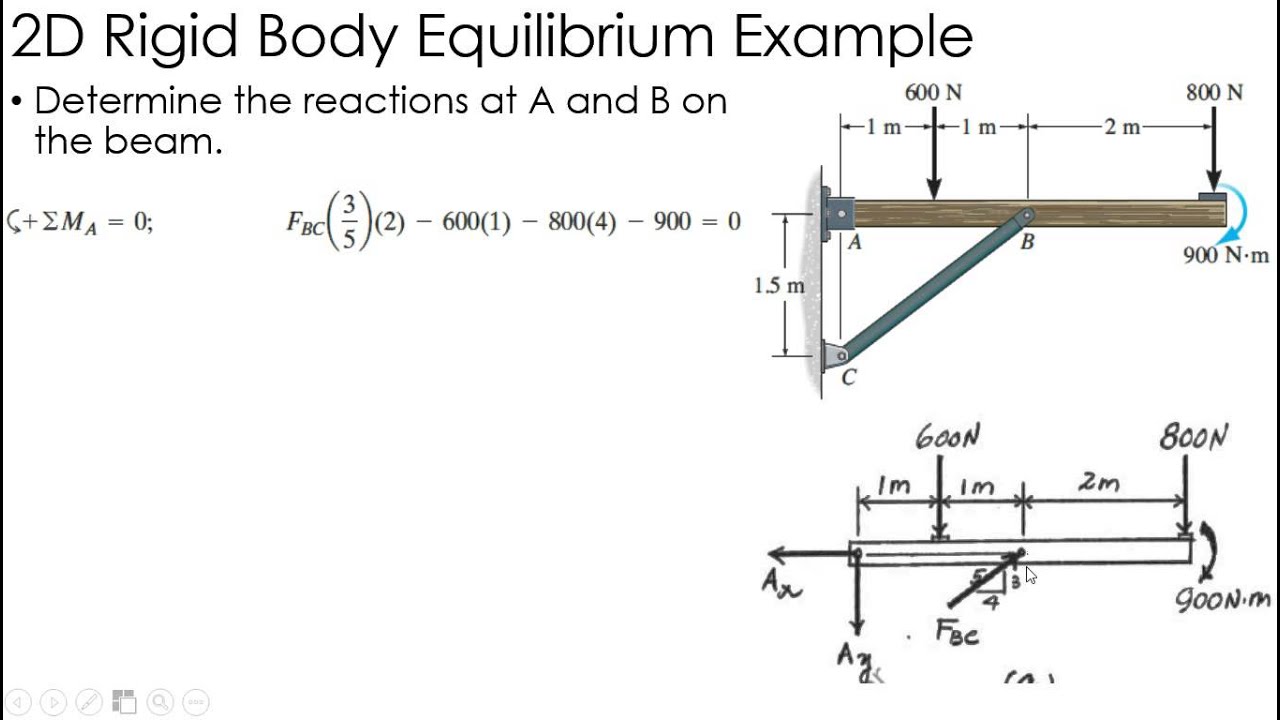
Statics Example 2D Rigid Body Equilibrium YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Yvasf_DLS8o/maxresdefault.jpg

15 4 Rigid Body Surface Collisions Video Lecture JPM YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LQKk2WLMe4A/maxresdefault.jpg

Ep 1 An Introduction To Rigid Bodies YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/bcMY8Jc7-dw/maxresdefault.jpg
The point where the whole mass of the body is suppose to be concentrated is called its center of mass The moment of inertia equal to the sum of the products of the mass of each particle in the body with the square of its distance from the axis of rotation It can be calculated as Learn more Center of mass brainly in question 5785557 Shear modulus of a perfectly rigid body is a zero b unity c infinity d non zero but unity Get the answers you need now Abhipsaaaa1128 Abhipsaaaa1128 31 03 2020
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Equations Of Motion For Rigid Body Systems Lesson 4 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/DNpsctGgdtw/maxresdefault.jpg

C4D Dynamics Simulation Rigid Body Soft Body Collider Body Dynamics
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SqCerFtNNmY/maxresdefault.jpg

https://brainly.in › question
The rigid body motion can be expressed as When a constraint is expressed by equalities it is termed as holonomic constraint and those who do not are called non holonomic constraints Again if the constraint is independent of time it is called scleronomic constraints and if it is dependent of time explicitly then it is called rheonomic

https://brainly.in › question
Rigid body is a body that does not get deformed or change its shape even due to the action of any external forces or loads In case of Rigid body the distance remains constant between any of the two points when the rigid body is under the action of loads

2015 Statics 19 Rigid Body Equilibrium 2D Supports with Closed

Equations Of Motion For Rigid Body Systems Lesson 4 YouTube
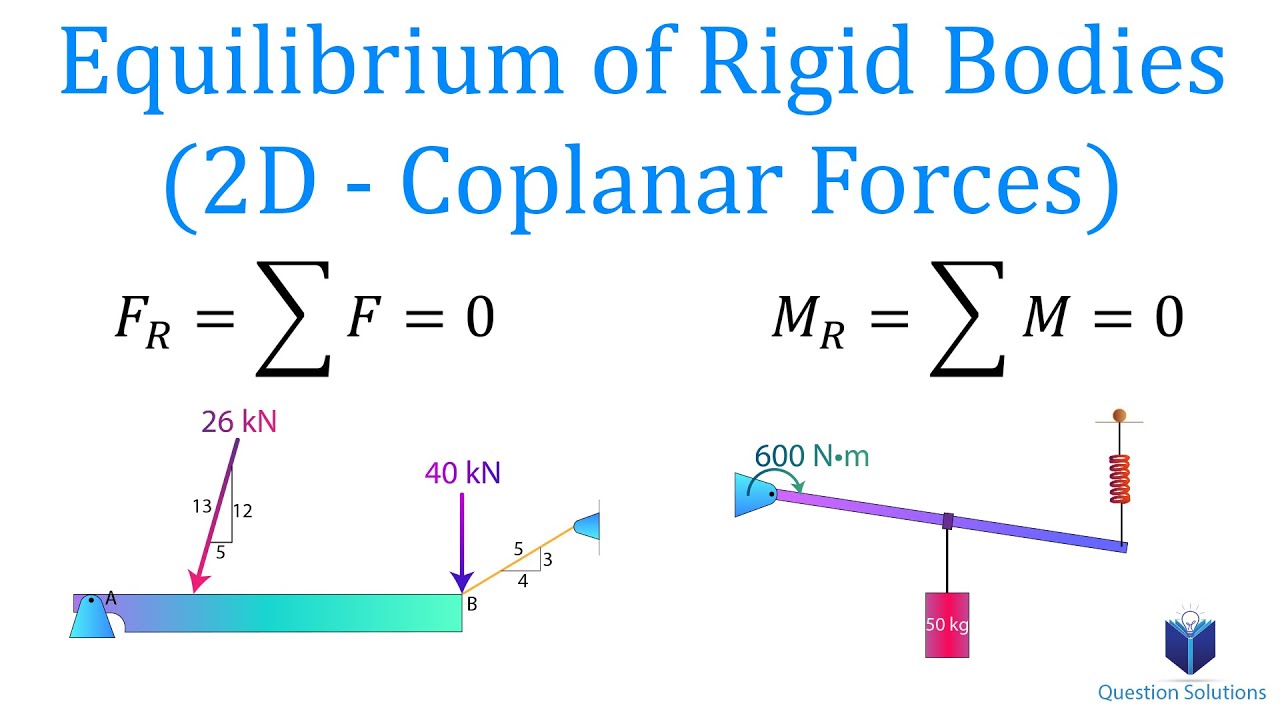
Equilibrium Of Rigid Bodies 2D Coplanar Forces Mechanics Statics
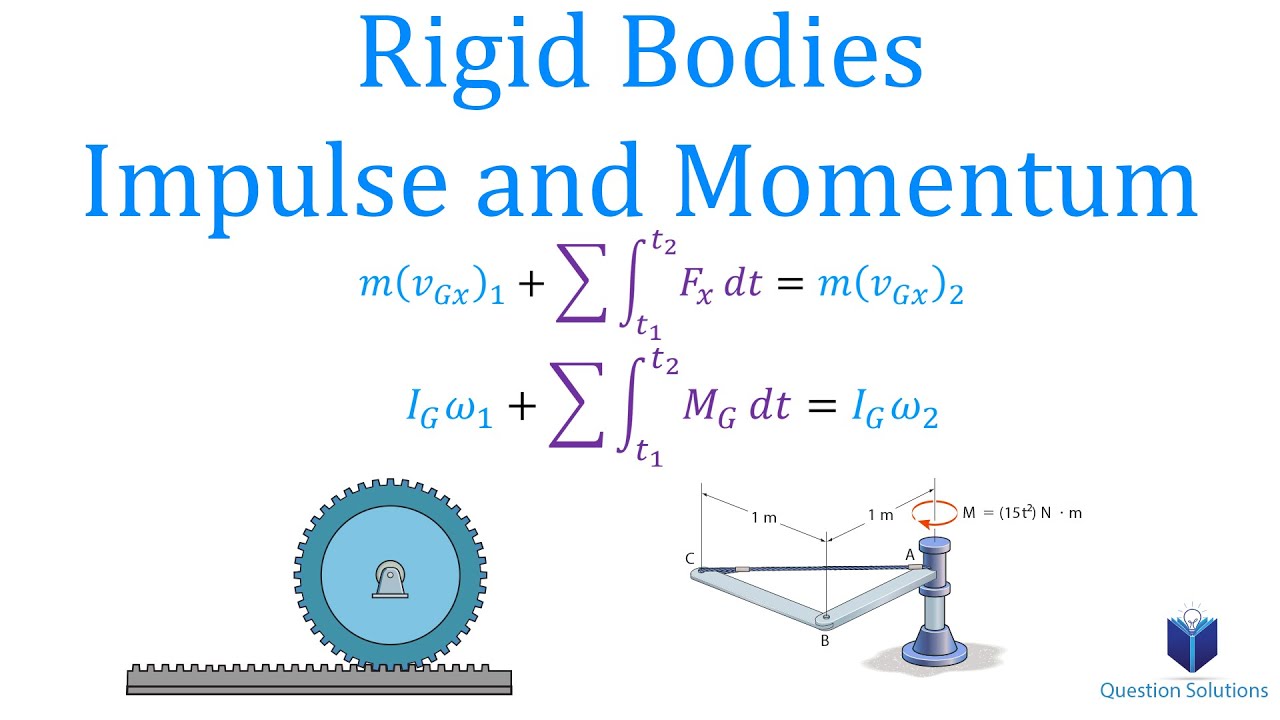
Rigid Bodies Impulse And Momentum Dynamics Learn To Solve Any Question

5 11 Equilibrium Of A Rigid Body Chapter 5 Hibbeler Statics 14th

Rigid Body Object Example 1 Ball Spiraling Down And Hitting Cylinders

Rigid Body Object Example 1 Ball Spiraling Down And Hitting Cylinders

11 1 Dynamics Rotation Of A Rigid Body YouTube

Difference Between Rigid Body And Resistant Body abhisheklectures
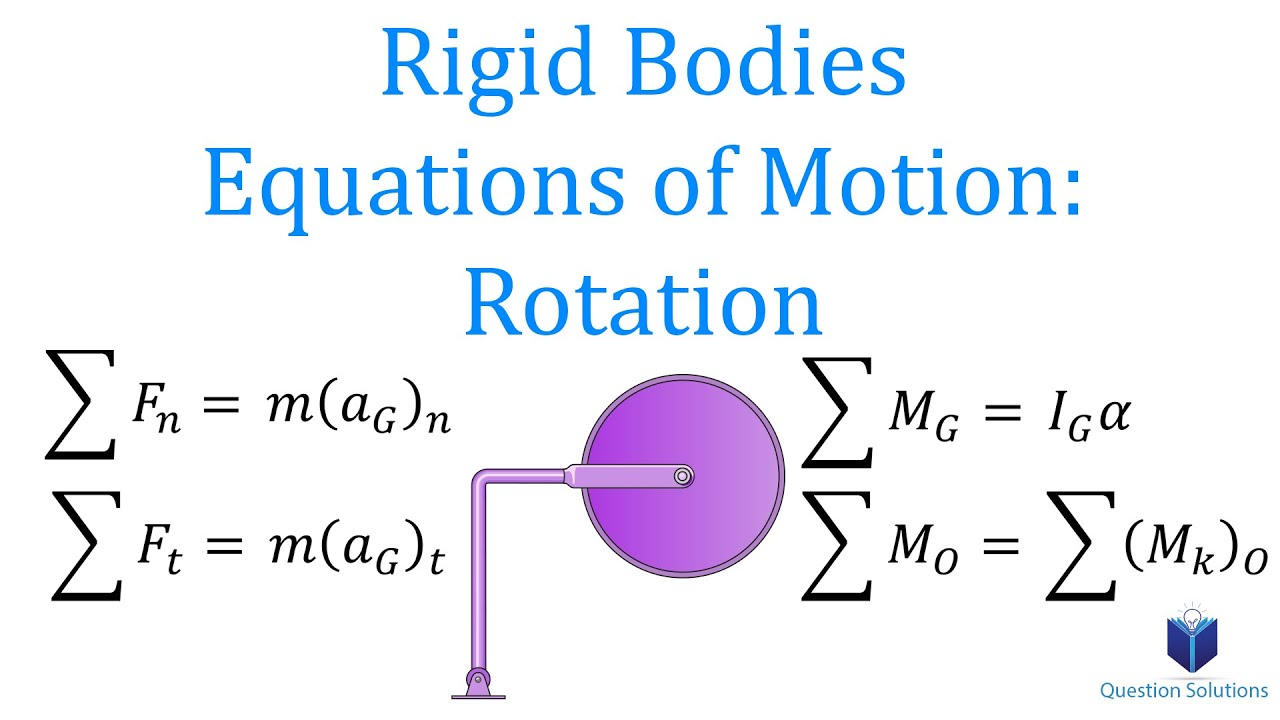
Rigid Bodies Equations Of Motion Rotation Learn To Solve Any Question
What Is Rigid Body - A system of two bodies of masses m and M being interconnected by a spring of stiffness k in its natural length moves towards a rigid wall on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in figure with a K E of system E